
Rhinoplasty (plastic nose) is the correction, restoration, correction of the structure of the nose using plastic surgery techniques. Used for medical and aesthetic reasons.
Although ongoing, nasal correction surgery is still considered one of the most difficult.
Nose repair surgery has been performed for thousands of years. Ancient manuscripts attest to the successful experience of such procedures long before our era.
Medicine has gone a step further than ancient physicians, and modern rhinoplasty is more of a cosmetic procedure than a medical necessity.
Indications for rhinoplasty
Each plastic surgery is a complex creative process that combines the problem of solving aesthetic problems with the preservation or restoration of functional features of a particular organ (in this case, that is nasal respiration).
Therefore, rhinoplasty can be performed for therapeutic and aesthetic purposes. The optimum age to run it is 25-35 years.
Medical indications are:
- congenital defects of the nasal septum;
- polyps and turbinate hypertrophy;
- traumatic injury and post -traumatic changes in bone, cartilage, physiology (due to uneven tissue development) or compensatory curvature of the nasal septum;
- obvious violation or the absence of the possibility of nasal breathing.
Changes in the correct anatomical structure of the nose very often lead to functional disorders and pathological conditions - shortness of breath, atrophy or hypertrophy of the nasal mucosa, rhinosinusitis, otitis media, frequent respiratory diseases, night snoring.
In addition, in children, such disabilities can cause chronic brain oxygen starvation, which leads not only to physical, but also mental retardation, and affects their mental development and behavioral reactions. Therefore, rhinoplasty can also be performed on children under 18 years of age.
More than 60% of the reason for rhinoplasty is the patient’s desire to improve the shape of the nose to achieve harmony of its appearance. Plastic surgeon services are becoming increasingly popular. Aesthetic indications for rhinoplasty are divided into two major groups:
- objective - unbalanced and unattractive size or shape of the nose;
- subjective, or psychological: there are no specific criteria for judging beauty, everyone has their own stereotypes, and therefore, just for personal reasons, he or she may not like his or her nose.
These reasons often affect people’s professional and personal relationships, give rise to complexes of dissatisfaction and low self-esteem, especially in women’s environments, causing social discomfort.
Rhinoplasty for aesthetic purposes is indicated in cases where there are:
- unbalanced nose size in relation to the whole face - too large or, conversely, too small;
- congenital or acquired defects;
- curvature of the nasal septum;
- nostrils widened, humped;
- fork, lowered or too high, the tip asymmetrical, as well as its incompatibility with the height of the nasal dorsum;
- saddle shape;
- unsatisfactory aesthetic results from previous operations.
In many cases, the medical and aesthetic indications are the same and are the result of the same anatomical defect.

Types of rhinoplasty
In accordance with the objectives achieved and techniques of performing surgical interventions, rhinoplasty is divided into:
- Reconstructive, the purpose is to restore anatomical disorders caused by improper intrauterine development, traumatic injury or disease.
- Aesthetics - correction of existing shortcomings.
According to the same criteria, there are several types of rhinoplasty:
- Reduction or enlargement of the nose.
- Backup alignment - saddle depression correction or bump removal
- Correction of aesthetic imperfections of the ends.
- Septum correction (septoplasty).
- Structural reconstruction after trauma.
All types of operations are divided into:
- main;
- seconds;
- repeated.
Access techniques
When performing rhinoplasty, depending on access options, the following techniques are used:
- Closed rhinoplasty,where incisions can occur in the nasal cavity. Closed access is divided into marginal (along the inner surface of the nasal wing), transseptal, inter- and transchondral. After the incision, the soft tissue is separated (separated) from the cartilage and bone that make up the skeleton, allowing you to freely perform the necessary manipulations. Closed rhinoplasty is less traumatic than open rhinoplasty and eliminates arterial damage and malnutrition, and postoperative scars are completely invisible, as they are located in the nasal cavity. It is used most often, especially for aesthetic rhinoplasty.
- Open rhinoplasty- incisions pass through the kolumella (the part of the skin that folds between the nasal openings) and on the nasal wings at their intersection with the lips. This technique is used in cases where it is not possible to accomplish the task in another way (closed). This allows you to raise the soft tissues and cartilage upwards, to gain adequate access to the inside of the nose and perform manipulations under constant visual control. Open rhinoplasty is required to correct very serious changes and technically complex and significant operations - significant nasal deformities, especially with lateral displacement; a combination of nasal defects with defects such as "cleft lip" or hard palate cleft; reconstruction using grafting. The disadvantages of open rhinoplasty are the formation of significant postoperative scars, as well as forced damage to the columella arteries, which results in significant and long -lasting postoperative tissue edema.
Rhinoplasty of any type is performed under one type of general anesthesia and usually lasts for 1-2 hours. Sometimes their duration can reach three or more hours.
How is rhinoplasty performed?
The operations are carried out in the following order:
- correction of the nasal septum is performed;
- if necessary, the nasal shell is reduced;
- the nasal hump is corrected if necessary to form an even profile;
- the bone is dissected and transplanted to narrow the nasal pyramid;
- straighten the nose;
- tip correction.
Rhinoplasty review
Nasal recurrence is considered if there is already surgical intervention in this area. The final formation of the nose after plastic surgery occurs in six months - 1 year. This period is optimal for re -operation. It runs when:
- the impossibility of achieving a goal in one level;
- unsatisfactory primary operation results;
- the need to correct problems that still exist after primary rhinoplasty.
According to world statistics, 25-30% of patients undergoing primary rhinoplasty require a second corrective surgery. This is considered normal. It usually lasts no more than half an hour and is performed under local anesthesia. Corrective revision rhinoplasty allows you to repair scar deficiencies and bring the shape of the nose to an aesthetic result that will meet the needs of surgeons and patients.
It is much more difficult to perform recurrent rhinoplasty in cases that are not good during recovery or are not good, which often depends on individual characteristics and complications. Such operations require more in -depth examination and more thorough preparation. They represent a complete plastic according to one option, but, as a rule, it turns out much more complicated and time consuming. Small deficiencies during repeated plastic surgery can lead to disruption of the end of the shape, not only, for example, the tip, but also on the overall deformation of the nose significantly.
Complications and preparation for surgery
The nose is considered one of the most difficult plastic surgeries, the outcome of which depends a lot on the skill and experience of the surgeon. Complications occur in 4-15% of cases. They can occur during surgery (bleeding, skin rupture, rupture of the muco-cartilaginous flap, violation of the integrity of the bone pyramid, bone fractures, etc. ) and postoperatively.
Possible complications after rhinoplasty:
- functioning - atrophic rhinitis, difficulty breathing nasal, loss of smell, temporary or permanent decrease or loss of sensitivity of the skin of the nose and upper lip;
- aesthetics - no changes or deterioration of previous deficiencies;
- psychology - patient dissatisfaction with the results of plastic surgery;
- infectious - prolonged swelling and inflammation, swelling;
- pigmentation of the nasal skin, formation of blood vessels, adhesion of mucous membranes and rough scars;
- recurrent nosebleeds and soft tissue or cartilage necrosis.
Preparation consists of:
- Consultation with a plastic surgeon, where the technical feasibility of meeting the patient’s wishes is determined.
- Conduct general studies - clinical and biochemical blood tests, blood clotting tests (coagulogram), general urine analysis, tests for hepatitis, HIV, syphilis (RW), ECG.
- Conduct (if necessary) special studies - pictures of the paranasal sinuses, endoscopic examination of the nasal cavity to identify corresponding anomalies and pathological changes.
- Computer simulations that allow patients to compare the initial condition of the nose with the results of future rhinoplasty.
- Consultation of therapists and specialists (in case of chronic illness).
- Examination by an anesthesiologist after all examinations.
- Refusal two weeks before surgery from taking drugs that affect the process of blood clotting - acetylsalicylic acid and its analogues, anticoagulants.
- Stop taking sedatives and sleeping pills on the day of the intervention.
Contraindications and recovery
Absolute contraindications for rhinoplasty:
- the presence of any chronic systemic disease in severe form (endocrine, cardiovascular, pulmonary);
- acute infectious diseases;
- blood clotting disorders;
- menstrual days.
Basic recovery from rhinoplasty lasts up to 3 weeks. Nevertheless, the term for the end of the full recovery period, when the results are evaluated, is determined by the doctor and is 6-12 months old. During this time, certain restrictions must be complied with.
After 1-1. 5 weeks after the intervention, the cast plaster and sutures were removed. For the first two weeks, do not wash with hot water or take a hot shower, as bleeding, bruising and swelling can occur by spreading to the entire face and neck. Sleep only on the back in an elevated position, which helps facilitate breathing and reduce swelling. In dusty places, it is recommended to wear face protection. Bending and lifting weights should be avoided.
Also, within 3 months, you must stop wearing glasses and wear a tight or heavy hat. You cannot visit the swimming pool and sunbathe for 3 months. In hot weather and in the sun, an umbrella or a wide -brimmed hat is recommended.
When planning options for rhinoplasty, experienced surgeons adhere to the principle of three types of restrictions: restrictions determined by the surgeon himself; restrictions imposed by patients; restrictions related to the patient’s condition and the anatomical features of his nose.
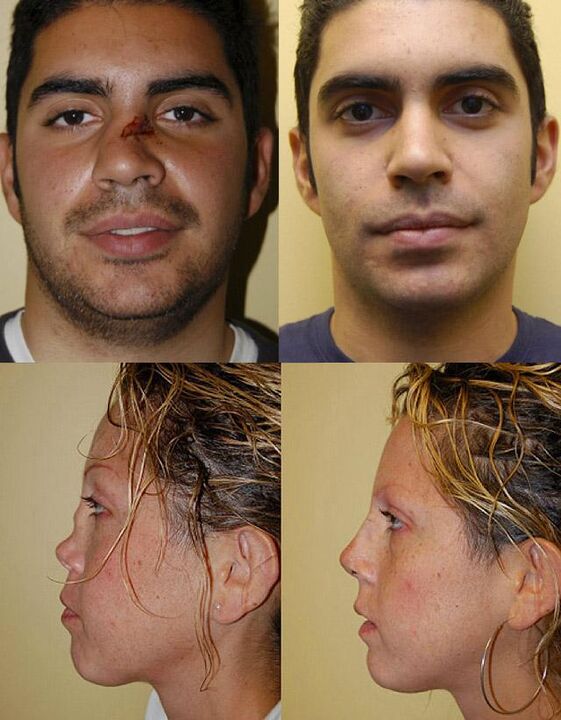


Price
Operating costs depend on the complexity of the correction.
Witnesses
Women's reviews
"I always had a complex because of the shape of my nose. It was too long, with bumps and the tip of the nose apparently splitting. Last year I decided to undergo rhinoplasty. If I had done it sooner, then my life would be now, Maybe better. They got rid of it allimperfections. They even restore the septum, a deficiency of which I myself do not know. My nose is perfect, as is my own. "
A man's review
"After I broke my nose a few times, my nasal septum shifted. I couldn't breathe normally, I snored badly at night. Diagnostics showed shortness of breath in my sleep. The nose looked ugly, it was moved to one side. I had to undergo rhinoplastyto straighten the nose and get rid of the problems associated with septum displacement. I did. I'm happy with the result. Now my nose is normal, like before the fracture. It's always breathing and I no longer snore. "
Rhinoplasty is not always a will, but often it is justified by objective need. It is important to choose a competent surgeon and make sure that you have no contraindications for the procedure.




















